Embark on a journey through the Bloodborne Pathogens Standard Precautions Quiz, an indispensable tool for healthcare professionals and anyone seeking to safeguard themselves from the risks of bloodborne pathogen transmission. This comprehensive quiz delves into the fundamental principles, practices, and protocols that form the cornerstone of effective infection control.
As you navigate through this quiz, you will gain a deeper understanding of the modes of transmission for bloodborne pathogens, the significance of universal precautions, and the proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Explore the critical role of hand hygiene, engineering controls, and work practice controls in minimizing the risk of exposure.
By completing this quiz, you will not only test your knowledge but also reinforce your commitment to protecting yourself and others from the hazards posed by bloodborne pathogens.
Bloodborne Pathogens Standard Precautions Overview
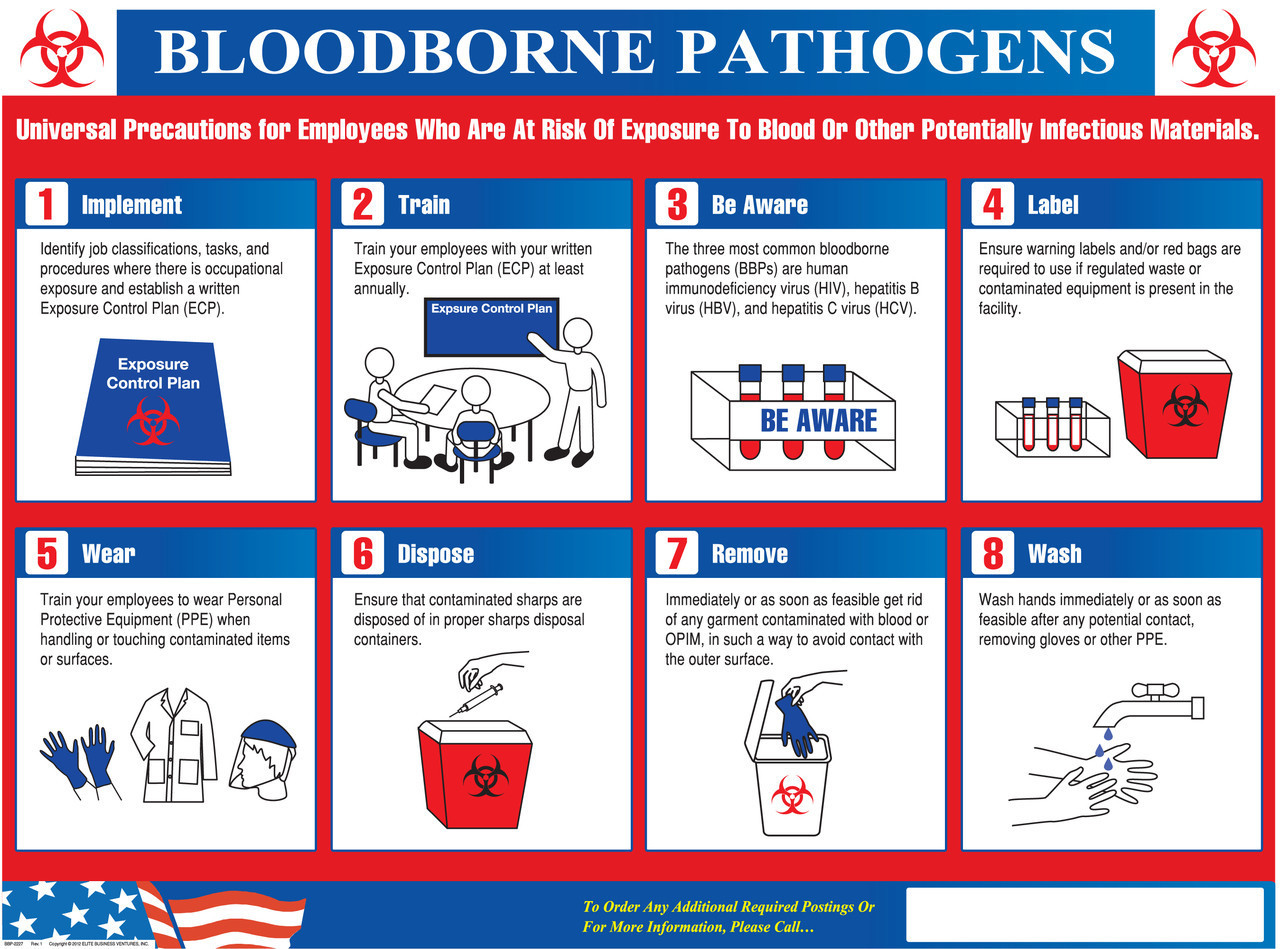
Bloodborne pathogens are microorganisms that can cause disease through contact with infected blood or other bodily fluids. Standard precautions are essential to prevent the transmission of these pathogens in healthcare settings.
Bloodborne pathogens can be transmitted through:
- Direct contact with infected blood or bodily fluids
- Contact with contaminated surfaces or objects
- Accidental needlesticks or sharps injuries
Universal Precautions
Universal precautions assume that all blood and bodily fluids are potentially infectious, regardless of the patient’s diagnosis or symptoms. This approach helps prevent the transmission of bloodborne pathogens by requiring the use of appropriate precautions for all patients.
Examples of universal precautions include:
- Hand hygiene
- Personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Safe handling of sharps
- Proper disposal of contaminated materials
Engineering and Work Practice Controls
Engineering controls are physical barriers or devices designed to reduce the risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens. These include:
- Sharps containers
- Needleless devices
- Closed systems for blood collection and transfusion
Work practice controls are procedures and policies that reduce the risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens. These include:
- Minimizing splashes and spills
- Using proper body mechanics when handling sharps
- Avoiding recapping needles
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PPE is worn to protect healthcare workers from exposure to bloodborne pathogens. Types of PPE include:
- Gloves
- Gowns
- Masks
- Eye protection
PPE must be used properly and disposed of safely to be effective.
Hand Hygiene
Hand hygiene is the most important measure for preventing the transmission of bloodborne pathogens. Proper handwashing techniques include:
- Using soap and water for at least 20 seconds
- Rubbing all surfaces of the hands
- Rinsing thoroughly
- Drying hands with a clean towel
Alcohol-based hand sanitizers can be used when soap and water are not available.
Management of Exposures, Bloodborne pathogens standard precautions quiz
If a healthcare worker is exposed to bloodborne pathogens, the following steps should be taken:
- Wash the exposed area with soap and water
- Report the exposure to the supervisor
- Seek medical evaluation
- Consider post-exposure prophylaxis
Post-exposure prophylaxis is medication that can help prevent infection after an exposure to bloodborne pathogens.
Training and Education
Regular training and education on bloodborne pathogen standard precautions are essential for healthcare workers to stay up-to-date on the latest recommendations and to ensure compliance.
Effective training programs should include:
- Information on the risks of bloodborne pathogens
- Instructions on proper infection control practices
- Demonstration of PPE use
- Opportunities for practice and feedback
Compliance and Monitoring
Compliance with bloodborne pathogen standard precautions is essential to protect healthcare workers and patients from infection. Methods for monitoring compliance include:
- Observation of work practices
- Review of infection control records
- Employee feedback
Compliance can be improved through education, training, and feedback.
Detailed FAQs: Bloodborne Pathogens Standard Precautions Quiz
What are the primary modes of transmission for bloodborne pathogens?
Bloodborne pathogens can be transmitted through contact with infected blood, bodily fluids, or contaminated surfaces.
Why is hand hygiene considered a critical component of bloodborne pathogen precautions?
Hand hygiene is essential because it removes pathogens from the hands, preventing their transmission to patients, healthcare workers, and the environment.
What are some examples of engineering controls used in bloodborne pathogen precautions?
Engineering controls include sharps containers for safe disposal of needles and other sharp objects, as well as needleless devices to reduce the risk of needlestick injuries.