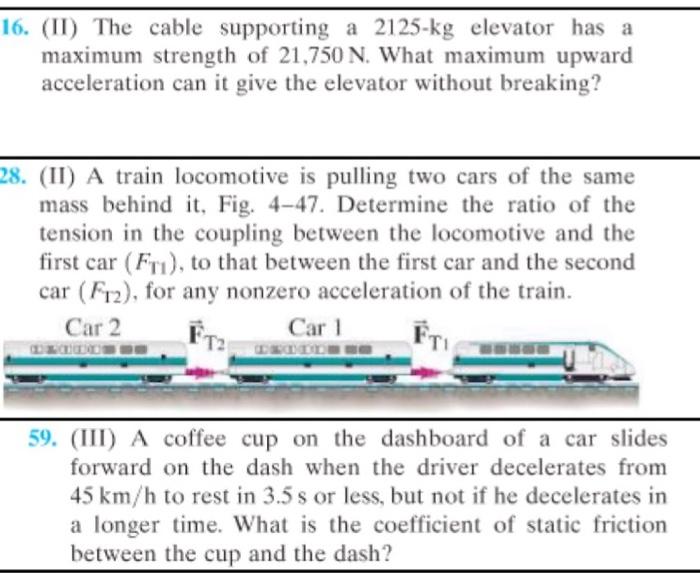
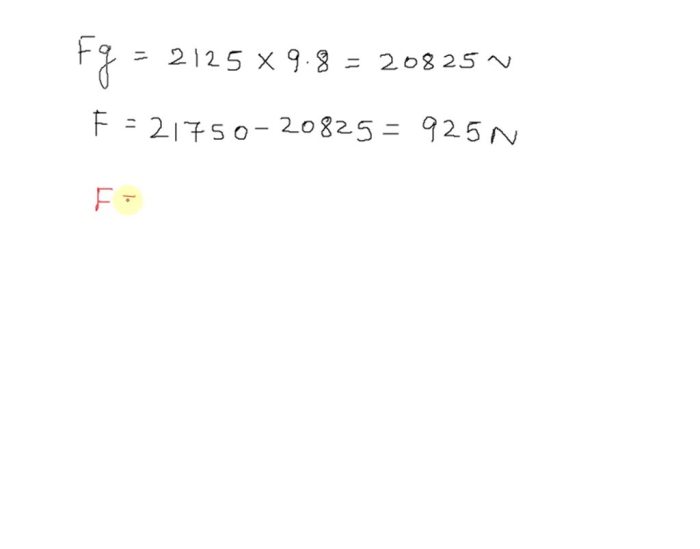The cable supporting a 2125 kg elevator is a critical component that ensures the safe and reliable operation of the elevator system. Understanding the specifications, design, installation, maintenance, and potential hazards associated with elevator cables is essential for ensuring the safety of passengers and maintaining the integrity of the elevator system.
This comprehensive guide delves into the technical aspects of elevator cables, providing detailed information on material composition, safety factors, design principles, installation procedures, and maintenance requirements. By understanding the intricacies of elevator cables, professionals can make informed decisions to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of elevator systems.
Cable Specifications: The Cable Supporting A 2125 Kg Elevator
The cable supporting a 2125 kg elevator must meet stringent tensile strength and elasticity requirements to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the elevator system.
Tensile Strength and Elasticity
- Tensile strength refers to the cable’s ability to resist breaking under tension.
- Elasticity refers to the cable’s ability to stretch and return to its original length when the load is removed.
Material Composition and Construction
- Elevator cables are typically made of high-strength steel alloys, such as carbon steel or stainless steel.
- The cable is constructed using multiple strands of wire twisted together to form a single unit.
- The number and thickness of the strands determine the overall strength and flexibility of the cable.
Safety Factors and Industry Standards, The cable supporting a 2125 kg elevator
- Safety factors are applied to the cable’s tensile strength to ensure that it can withstand the maximum load it may encounter during operation.
- Industry standards, such as those set by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), provide guidelines for the design and selection of elevator cables.
Cable Design
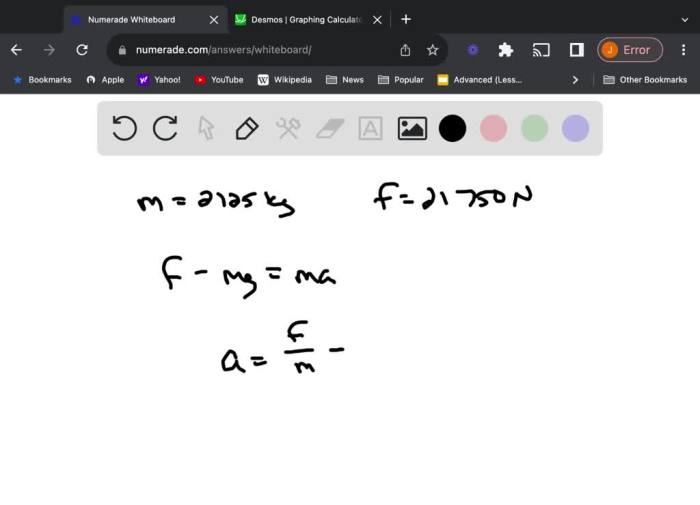
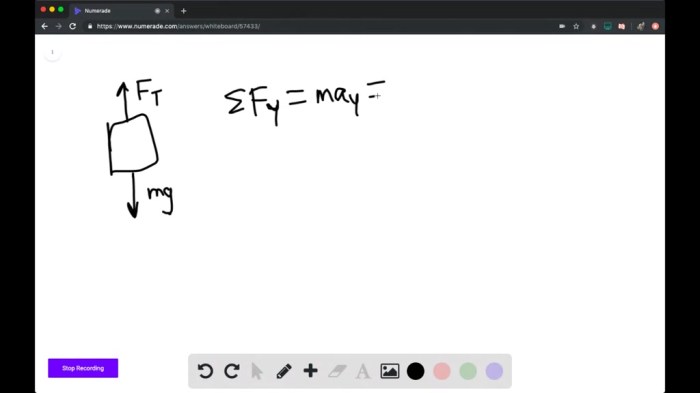
The design of the cable is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of the elevator system.
Principles of Cable Design
- The cable must be strong enough to support the weight of the elevator and its payload.
- The cable must be flexible enough to allow for smooth movement of the elevator.
- The cable must be resistant to wear and corrosion.
Factors Influencing Cable Diameter, Length, and Configuration
- The diameter of the cable is determined by the tensile strength required.
- The length of the cable is determined by the height of the elevator shaft.
- The configuration of the cable, such as the number of strands and the lay of the strands, affects the flexibility and strength of the cable.
Use of Pulleys, Sheaves, and Other Components
- Pulleys and sheaves are used to change the direction of the cable and reduce friction.
- Other components, such as tensioners and anchors, are used to ensure proper tensioning and securement of the cable.
Expert Answers
What is the tensile strength requirement for the cable supporting a 2125 kg elevator?
The tensile strength of the cable must be sufficient to support the weight of the elevator, the passengers, and any additional loads. The specific tensile strength requirement will vary depending on the specific elevator system and applicable safety factors.
What are the key factors that influence the design of an elevator cable?
The design of an elevator cable is influenced by factors such as the weight of the elevator, the height of the elevator shaft, the speed of the elevator, and the desired safety factor. The cable diameter, length, and configuration must be carefully calculated to ensure the cable can safely support the elevator under all operating conditions.
What are the potential hazards associated with elevator cables?
Potential hazards associated with elevator cables include cable breakage, cable fraying, and cable corrosion. These hazards can lead to elevator malfunction, passenger entrapment, and even injury or death. Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to identify and mitigate these hazards.