Embarking on a journey through Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Answer Key, we delve into the fundamental building blocks of life. Cells, the microscopic units of life, and tissues, the organized assemblies of cells, form the foundation of all living organisms.
This chapter provides a comprehensive exploration of their structure, function, and interactions, unveiling the intricate tapestry of life’s construction.
Through a meticulous examination of cell organelles, tissue types, and their dynamic interplay, we uncover the secrets of cellular communication, environmental adaptation, and tissue homeostasis. This knowledge empowers us to understand the complexities of human health and disease, paving the way for groundbreaking advancements in medicine and biology.
1. Introduction: Chapter 3 Cells And Tissues Answer Key
Cells are the fundamental units of life and are the building blocks of all living organisms. Tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform a specific function.
Cells are the smallest unit of life that can exist independently. They are responsible for all of the activities of life, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and response to stimuli.
Tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform a specific function. There are four main types of tissues in the human body: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
2. Cell Structure and Function, Chapter 3 cells and tissues answer key
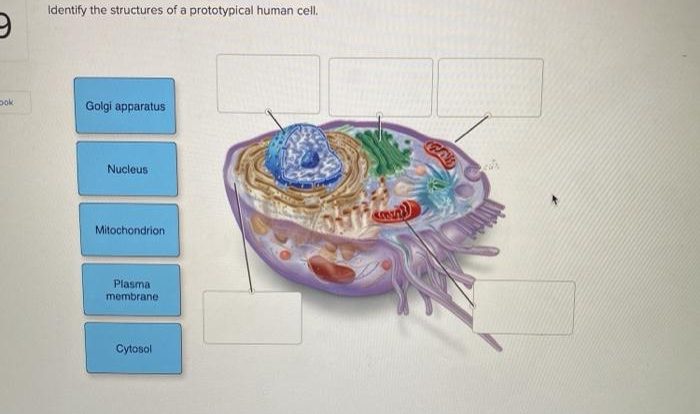
Cells are composed of a variety of organelles, each of which has a specific function.
- The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic material.
- The endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for protein synthesis.
- The Golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins.
- The mitochondria produce energy for the cell.
- The lysosomes are responsible for digesting waste products.
There are many different types of cells in the human body, each with a specialized function. Some of the most common types of cells include:
- Epithelial cells line the surfaces of the body and protect the body from the environment.
- Connective tissue cells support and connect the different tissues of the body.
- Muscle cells allow the body to move.
- Nervous tissue cells transmit information throughout the body.
Q&A
What is the relationship between cells and tissues?
Cells are the basic unit of life, and tissues are groups of similar cells that perform a specific function.
What are the different types of cells?
There are many different types of cells, including muscle cells, nerve cells, and epithelial cells.
What are the different types of tissues?
There are four main types of tissues: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
How do cells communicate with each other?
Cells communicate with each other through chemical signals, electrical signals, and physical contact.
How do cells interact with their environment?
Cells interact with their environment through their cell membrane, which allows them to exchange nutrients and waste products with their surroundings.