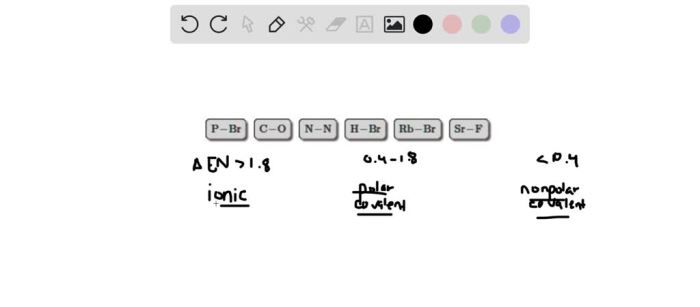
Drag the appropriate bonded atoms to their respective bins, an interactive exercise, provides a comprehensive understanding of the characteristics, classification, and applications of bonded atoms. This guide delves into the fundamental principles of atomic bonding, empowering learners to identify, categorize, and utilize bonded atoms effectively.
Through a detailed exploration of electronegativity, bond types, and practical applications, this guide equips learners with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the complex world of atomic interactions.
Identifying Bonded Atoms
Bonded atoms are atoms that are connected to each other by chemical bonds. The characteristics that define bonded atoms include:
- They have overlapping electron orbitals.
- They share electrons between them.
- They have a net attraction between their nuclei and electrons.
There are three main types of bonds that can form between atoms: covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and metallic bonds.
- Covalent bondsare formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
- Ionic bondsare formed when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom.
- Metallic bondsare formed when the metal atoms share their valence electrons in a sea of electrons.
The type of bond that forms between two atoms is determined by the electronegativity of the atoms. Electronegativity is a measure of how strongly an atom attracts electrons. The more electronegative an atom, the more strongly it attracts electrons.
Classifying Bonded Atoms
| Element | Symbol | Atomic Number | Electronegativity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H | 1 | 2.20 |
| Carbon | C | 6 | 2.55 |
| Nitrogen | N | 7 | 3.04 |
| Oxygen | O | 8 | 3.44 |
| Fluorine | F | 9 | 3.98 |
| Sodium | Na | 11 | 0.93 |
| Magnesium | Mg | 12 | 1.31 |
| Aluminum | Al | 13 | 1.61 |
| Silicon | Si | 14 | 1.90 |
| Chlorine | Cl | 17 | 3.16 |
The electronegativity values in the table can be used to predict the type of bond that will form between two atoms. If the electronegativity difference between the two atoms is small, a covalent bond will form. If the electronegativity difference is large, an ionic bond will form.
If the electronegativity difference is very large, a metallic bond will form.
Sorting Bonded Atoms
Bonded atoms can be sorted into different categories based on their electronegativity, atomic number, and bond type. The following flowchart illustrates the steps involved in sorting bonded atoms:
- Determine the electronegativity of each atom.
- Calculate the electronegativity difference between the two atoms.
- Use the electronegativity difference to determine the type of bond that has formed.
- Sort the atoms into the appropriate category based on the type of bond that has formed.
For example, if you have two atoms with electronegativities of 2.5 and 3.5, the electronegativity difference would be 1.0. This indicates that a covalent bond has formed between the two atoms. The atoms would be sorted into the category of “covalently bonded atoms.”
Applications of Sorting Bonded Atoms, Drag the appropriate bonded atoms to their respective bins
Sorting bonded atoms has a number of practical applications, including:
- Materials science:Sorting bonded atoms can be used to design new materials with specific properties. For example, by sorting atoms based on their electronegativity, it is possible to design materials that are strong, lightweight, and resistant to corrosion.
- Chemistry:Sorting bonded atoms can be used to understand the chemical reactions that occur between different atoms. For example, by sorting atoms based on their atomic number, it is possible to predict the products of a chemical reaction.
- Biochemistry:Sorting bonded atoms can be used to understand the structure and function of biological molecules. For example, by sorting atoms based on their electronegativity, it is possible to identify the active sites of enzymes.
Top FAQs: Drag The Appropriate Bonded Atoms To Their Respective Bins
What are the different types of atomic bonds?
Covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds are the primary types of atomic bonds.
How does electronegativity influence the type of bond formed?
Electronegativity determines the tendency of an atom to attract electrons. Atoms with high electronegativity tend to form ionic bonds, while atoms with low electronegativity tend to form covalent bonds.
What are the practical applications of sorting bonded atoms?
Sorting bonded atoms has applications in materials science, chemistry, and biochemistry. It aids in the design of new materials with specific properties and advances scientific research and technological development.