Correctly label the different filaments of a sarcomere – Correctly labeling the different filaments of a sarcomere is essential for understanding the fundamental mechanisms of muscle contraction. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the three main filaments found within a sarcomere: thin, thick, and titin filaments, exploring their composition, structure, arrangement, and function.
Delving into the intricate details of each filament, we will uncover the remarkable interplay between these structures and their crucial roles in muscle contraction, paving the way for a deeper comprehension of muscle physiology and its implications in movement and overall health.
Identify the Different Filaments of a Sarcomere
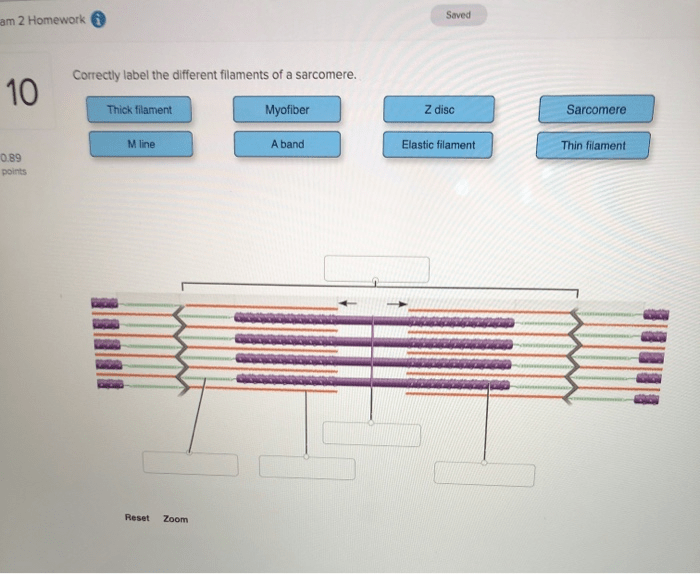
A sarcomere is the basic unit of contraction in a muscle fiber. It is composed of three main types of filaments: thin filaments, thick filaments, and titin filaments.
Thin Filaments
Thin filaments are made up of the protein actin. They are about 7 nm in diameter and are arranged in a helical pattern around the thick filaments.
Thick Filaments, Correctly label the different filaments of a sarcomere
Thick filaments are made up of the protein myosin. They are about 15 nm in diameter and are arranged in a hexagonal pattern in the center of the sarcomere.
Titin Filaments
Titin filaments are made up of the protein titin. They are about 1 nm in diameter and extend from the Z-disk to the M-line of the sarcomere. Titin filaments help to maintain the sarcomere structure and prevent the thick filaments from sliding too far apart during muscle contraction.
Label the Filaments in a Sarcomere Diagram
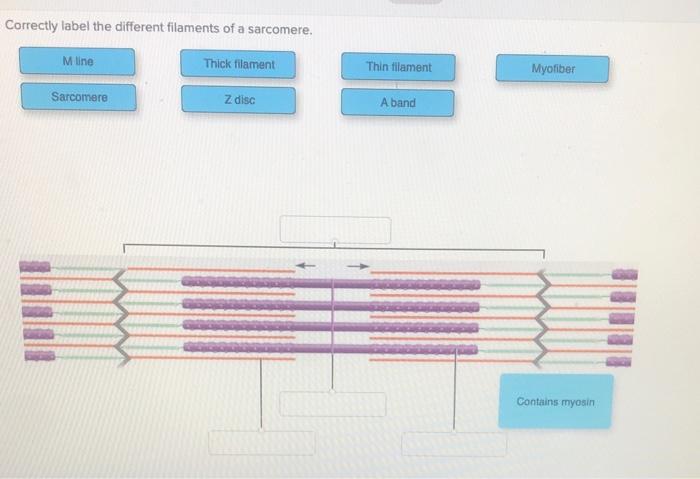
The following diagram shows the arrangement of the thin, thick, and titin filaments in a sarcomere.
[Diagram sarcomere]
The thin filaments are shown in red, the thick filaments are shown in blue, and the titin filaments are shown in green.
Describe the Arrangement of Filaments in a Sarcomere
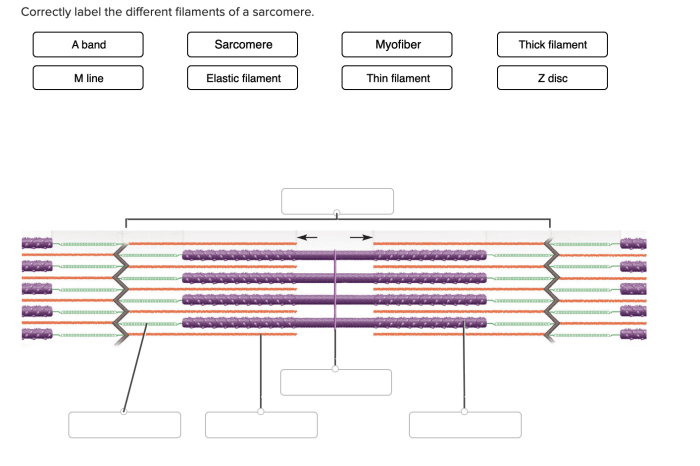
The thin filaments are arranged in a helical pattern around the thick filaments. The thick filaments are arranged in a hexagonal pattern in the center of the sarcomere. The titin filaments extend from the Z-disk to the M-line of the sarcomere.
The arrangement of the filaments is important for muscle contraction. When a muscle contracts, the thin filaments slide over the thick filaments, causing the sarcomere to shorten.
Compare the Function of Different Filaments in Muscle Contraction
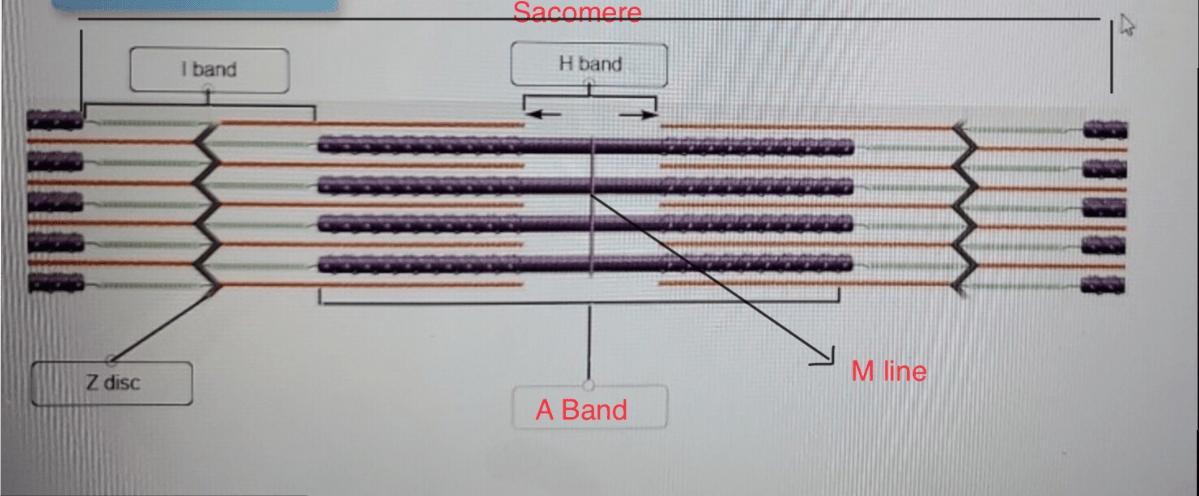
The thin filaments are responsible for binding to the myosin heads on the thick filaments. This binding triggers the power stroke, which is the movement of the myosin heads towards the center of the sarcomere.
The thick filaments provide the force for muscle contraction. The myosin heads on the thick filaments bind to the thin filaments and pull them towards the center of the sarcomere.
The titin filaments help to maintain the sarcomere structure and prevent the thick filaments from sliding too far apart during muscle contraction.
Illustrate the Sliding Filament Model of Muscle Contraction
The sliding filament model of muscle contraction is a model that explains how the thin and thick filaments interact to cause muscle contraction.
According to the sliding filament model, when a muscle contracts, the thin filaments slide over the thick filaments, causing the sarcomere to shorten.
[Diagram sliding filament model]
The sliding filament model is supported by a number of experimental observations. For example, studies have shown that the length of the sarcomere decreases when a muscle contracts.
Helpful Answers: Correctly Label The Different Filaments Of A Sarcomere
What is the role of thin filaments in muscle contraction?
Thin filaments, composed of actin, play a crucial role in muscle contraction by interacting with myosin heads on thick filaments, initiating the sliding filament mechanism that shortens the sarcomere.
How do thick filaments contribute to muscle contraction?
Thick filaments, composed of myosin, are the primary force generators in muscle contraction. Myosin heads extend from the thick filaments, binding to actin on thin filaments and undergoing a conformational change that powers the sliding filament mechanism.
What is the function of titin filaments in muscle contraction?
Titin filaments, giant proteins that span the length of the sarcomere, play a vital role in maintaining sarcomere structure, providing elasticity and preventing overstretching during muscle contraction.