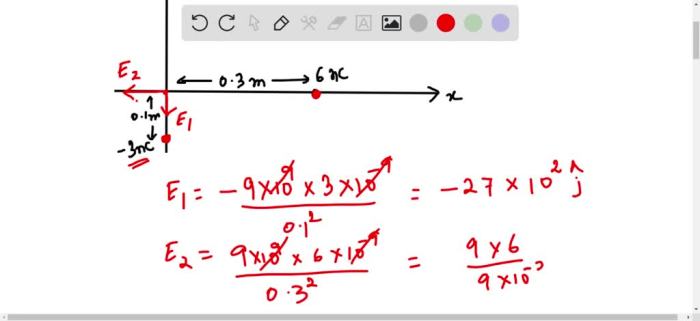
Consider the arrangement of point charges in the figure. – Consider the arrangement of point charges in the figure: this intriguing topic unveils the fascinating realm of electrostatics, where the behavior of charged particles captivates our curiosity. Point charges, idealized as particles with negligible size and concentrated charge, serve as fundamental building blocks in understanding electric fields, potential energy, and their diverse applications.
Delving into the intricacies of point charge arrangements, we embark on a journey to unravel the intricate dance of electric forces. We explore the factors that govern the strength and direction of electric fields, unlocking the secrets of potential energy and its dependence on charge configurations.
Along the way, we uncover practical applications that harness the principles of point charges, revolutionizing fields from electronics to medical imaging.
Arrangement of Point Charges: Consider The Arrangement Of Point Charges In The Figure.
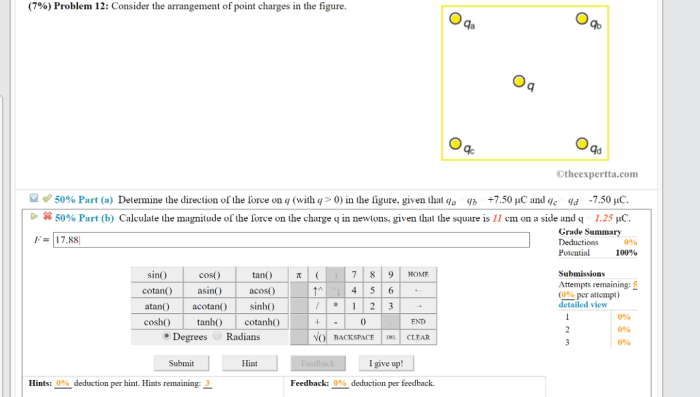
Point charges are idealized objects that carry a specific amount of electric charge. They are useful for understanding the behavior of electric fields and potentials. Point charges can be either positive or negative, and they can be arranged in various ways.
The arrangement of point charges can have a significant impact on the electric field and potential energy distribution. For example, two point charges of the same sign will repel each other, while two point charges of opposite sign will attract each other.
The strength of the electric field and potential energy will also depend on the distance between the point charges.
Electric Field Due to Point Charges
Point charges create an electric field around them. The electric field is a vector quantity that describes the strength and direction of the electric force that a point charge would experience at a given location.
The electric field due to a point charge can be calculated using the following equation:
“`E = k
q / r^2
“`
where:
- E is the electric field (in newtons per coulomb)
- k is Coulomb’s constant (8.98755 × 10^9 N⋅m^2/C^2)
- q is the charge of the point charge (in coulombs)
- r is the distance from the point charge to the location where the electric field is being calculated (in meters)
The electric field due to a point charge is a radial field, which means that it points directly away from the point charge for positive charges and directly towards the point charge for negative charges.
Potential Energy of Point Charges, Consider the arrangement of point charges in the figure.
Point charges also have potential energy. The potential energy of a point charge is the amount of work that would be required to bring another point charge from infinity to a given location near the first point charge.
The potential energy of a point charge can be calculated using the following equation:
“`U = k
- q
- q’ / r
“`
where:
- U is the potential energy (in joules)
- k is Coulomb’s constant (8.98755 × 10^9 N⋅m^2/C^2)
- q and q’ are the charges of the two point charges (in coulombs)
- r is the distance between the two point charges (in meters)
The potential energy of two point charges is positive if the charges have the same sign and negative if the charges have opposite signs.
Applications of Point Charges
Point charges are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Electrostatic precipitators, which remove particulate matter from the air
- Laser printers, which use point charges to attract toner particles to the paper
- Photocopiers, which use point charges to transfer toner particles from a drum to the paper
Point charges are also used in a variety of electronic devices, such as transistors and capacitors.
FAQ
What is the significance of point charges in understanding electrostatics?
Point charges provide a simplified model for analyzing electric fields and potential energy, allowing us to gain insights into the behavior of charged particles and their interactions.
How does the arrangement of point charges affect the electric field?
The arrangement of point charges determines the direction and strength of the electric field at different points in space, influencing the forces experienced by other charged particles.
What factors influence the potential energy of point charges?
The potential energy of point charges depends on their charges, the distance between them, and the permittivity of the surrounding medium.