Quantitative methods in psychology rutgers form the backbone of psychological research, providing researchers with powerful tools to understand and measure psychological phenomena. From descriptive statistics to advanced multivariate analysis, these methods enable psychologists to gather, analyze, and interpret data to gain insights into the human mind and behavior.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the nature and scope of quantitative methods in psychology, exploring their advantages and disadvantages, as well as the different types and applications of these methods. We also discuss the ethical considerations researchers must adhere to when using quantitative methods and provide resources for learning and applying these techniques effectively.
Quantitative Methods in Psychology Overview: Quantitative Methods In Psychology Rutgers
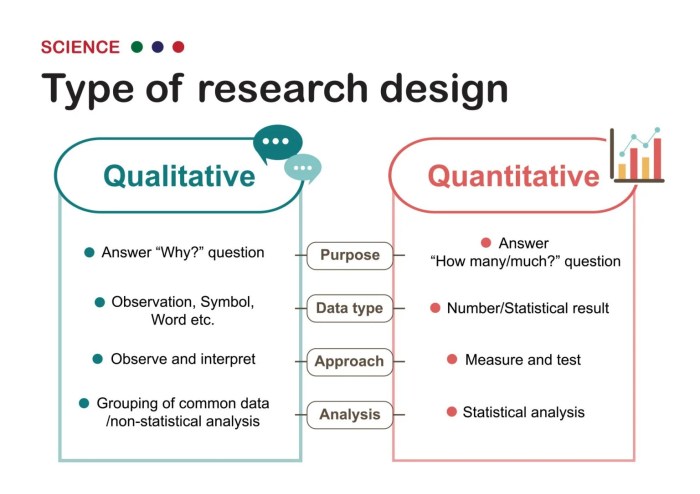
Quantitative methods are a fundamental aspect of psychological research, providing researchers with powerful tools to collect, analyze, and interpret data. These methods allow psychologists to quantify and measure psychological phenomena, making it possible to draw inferences and test hypotheses.
Quantitative methods are used extensively in various areas of psychology, including cognitive psychology, developmental psychology, social psychology, and clinical psychology. They enable researchers to investigate a wide range of psychological phenomena, such as the effects of different treatments on mental health, the cognitive processes involved in memory and learning, and the social factors that influence behavior.
The advantages of using quantitative methods in psychology include the ability to provide objective and reliable data, test hypotheses with statistical significance, and generalize findings to larger populations. However, it is important to note that quantitative methods also have limitations, such as the potential for bias and the inability to capture the richness and complexity of human experience.
Types of Quantitative Methods in Psychology
There are various types of quantitative methods used in psychology, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. These methods can be broadly categorized into three main types:
- Descriptive statistics: These methods are used to summarize and describe data, providing information about central tendencies, variability, and distributions.
- Inferential statistics: These methods allow researchers to make inferences about a larger population based on a sample, enabling them to test hypotheses and draw conclusions.
- Multivariate analysis: These methods are used to analyze complex relationships between multiple variables, providing insights into the underlying structure and dynamics of psychological phenomena.
Applications of Quantitative Methods in Psychology
Quantitative methods have played a pivotal role in advancing the field of psychology, contributing to a deeper understanding of psychological phenomena and informing the development of effective interventions.
- In cognitive psychology, quantitative methods have been used to investigate the processes involved in attention, memory, and decision-making.
- In developmental psychology, quantitative methods have been used to track changes in cognitive abilities, social development, and emotional regulation throughout the lifespan.
- In social psychology, quantitative methods have been used to study the effects of social influence, group dynamics, and prejudice.
- In clinical psychology, quantitative methods have been used to evaluate the effectiveness of different therapeutic approaches and to identify risk factors for mental health disorders.
Ethical Considerations in Using Quantitative Methods in Psychology, Quantitative methods in psychology rutgers
When using quantitative methods in psychology, researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines to ensure the responsible and ethical conduct of research.
- Informed consent: Participants must be fully informed about the purpose of the study, the procedures involved, and their rights as participants.
- Data privacy: Researchers must protect the confidentiality and privacy of participants’ data, ensuring that it is not disclosed without their consent.
- Avoiding bias: Researchers must take steps to minimize bias in their research design, data collection, and analysis, ensuring that the findings are accurate and unbiased.
Resources for Learning Quantitative Methods in Psychology
There are various resources available for learning quantitative methods in psychology, including books, online courses, and workshops.
- Books: There are numerous textbooks and manuals available that provide comprehensive coverage of quantitative methods in psychology, such as “Quantitative Psychology: An Introduction for the Social and Behavioral Sciences” by Cohen, Cohen, West, and Aiken.
- Online courses: Many universities and online platforms offer online courses in quantitative methods, providing a convenient and flexible way to learn the subject.
- Workshops: Workshops and seminars are also available, providing hands-on training and opportunities to apply quantitative methods to real-world research projects.
The Quantitative Methods in Psychology program at Rutgers University offers a rigorous curriculum that prepares students with a strong foundation in quantitative research methods, statistical analysis, and data interpretation. The program provides opportunities for students to engage in hands-on research experiences and to develop advanced skills in quantitative analysis.
Q&A
What are the advantages of using quantitative methods in psychology?
Quantitative methods offer objectivity, precision, and the ability to generalize findings to larger populations, making them essential for hypothesis testing and establishing causal relationships.
What are the disadvantages of using quantitative methods in psychology?
Quantitative methods can be limited in their ability to capture the complexity and richness of human behavior and may overlook important qualitative aspects of psychological phenomena.
What are the different types of quantitative methods used in psychology?
Common types of quantitative methods include descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and multivariate analysis, each with its own strengths and weaknesses for different research purposes.
What are the ethical considerations researchers must take into account when using quantitative methods in psychology?
Researchers must ensure informed consent, protect data privacy, and avoid bias in research design and data analysis to maintain ethical standards in quantitative psychological research.


