Unveiling the macromolecule testing lab answer key, this guide embarks on an illuminating journey into the intricate world of macromolecule analysis, empowering readers with a comprehensive understanding of its methods, applications, and significance.
Delving into the depths of macromolecule testing, we unravel the diverse techniques employed to scrutinize these complex biomolecules, exploring their underlying principles, advantages, and limitations. Moreover, we navigate the step-by-step procedures involved in conducting macromolecule tests, ensuring accuracy and reliability through meticulous attention to detail.
Macromolecule Definition
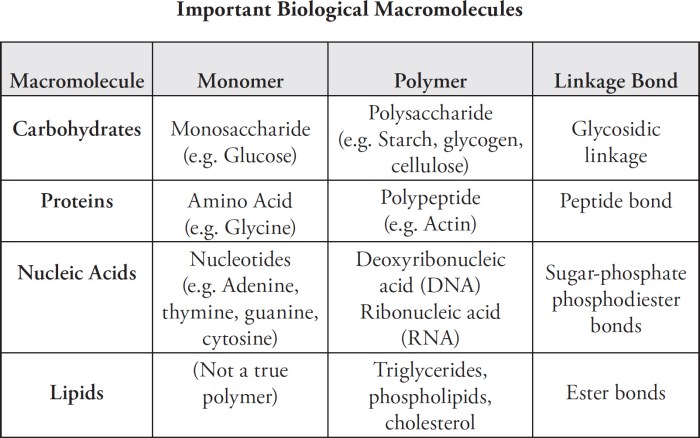
Macromolecules are large, complex molecules that play a crucial role in the structure and function of living organisms. They are composed of numerous smaller molecules, called monomers, which are linked together by covalent bonds.
Examples of macromolecules include:
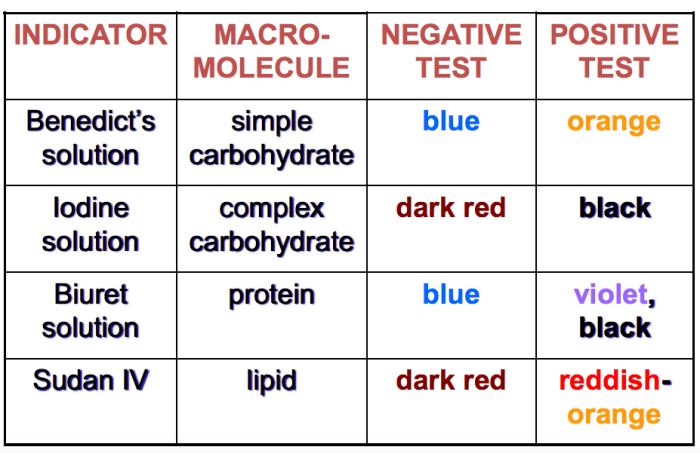
- Proteins: Composed of amino acids, proteins are involved in a wide range of cellular functions, such as catalysis, transport, and structural support.
- Carbohydrates: Composed of sugars, carbohydrates provide energy and structural support for cells.
- Lipids: Composed of fatty acids, lipids serve as energy stores, insulation, and membrane components.
- Nucleic acids: Composed of nucleotides, nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information.
Macromolecule Testing Methods
Various methods are used to test macromolecules, each with its own principles, advantages, and disadvantages:
- Gel electrophoresis: Separates macromolecules based on their size and charge.
- Chromatography: Separates macromolecules based on their affinity for different phases.
- Mass spectrometry: Determines the mass-to-charge ratio of macromolecules.
- Spectrophotometry: Measures the absorption or emission of light by macromolecules.
- Immunoassays: Use antibodies to detect specific macromolecules.
Macromolecule Testing Procedures, Macromolecule testing lab answer key
Macromolecule testing procedures vary depending on the method used. General steps may include:
- Sample preparation: Extracting and purifying macromolecules from a sample.
- Separation: Using appropriate techniques to separate macromolecules based on their properties.
- Detection: Using specific methods to detect and quantify the macromolecules of interest.
- Data analysis: Interpreting the results and drawing conclusions.
Safety precautions should be strictly followed, including proper handling of chemicals, wearing protective gear, and adhering to laboratory protocols.
FAQ Insights: Macromolecule Testing Lab Answer Key
What is the significance of macromolecule testing?
Macromolecule testing plays a vital role in various scientific disciplines, including biochemistry, genetics, and medicine. It enables researchers to analyze the structure, function, and interactions of macromolecules, providing insights into cellular processes, disease mechanisms, and potential therapeutic interventions.
How does macromolecule testing contribute to drug development?
Macromolecule testing is essential in the pharmaceutical industry for evaluating the efficacy and safety of new drug candidates. By studying the interactions between drugs and macromolecules, researchers can optimize drug design, predict potential side effects, and ensure the development of effective and safe therapies.
What are the challenges associated with macromolecule testing?
Macromolecule testing can be complex and time-consuming due to the large size and intricate structures of macromolecules. Additionally, the choice of appropriate testing methods and the interpretation of results require specialized expertise and experience.